
Temperature Measurement & Control Solutions
At Clipper Controls, we provide a full range of temperature measurement and control solutions designed to meet the demanding needs of industrial, utility, and environmental applications. From precise sensor technologies to robust transmitters and controllers, our products help ensure reliable monitoring, accurate process control, and consistent system performance. Whether you're working with high-temperature processes, sensitive environmental conditions, or harsh field environments, we offer proven solutions backed by technical expertise and strong manufacturer partnerships.
Temperature Sensors
Thermocouples
Application: Thermocouples are rugged and versatile temperature sensors used in high-temperature and dynamic environments. With fast response and the ability to measure up to 1,800°C depending on type, they are commonly installed in combustion systems, heat exchangers, turbines, and exhaust stacks. Their durability under thermal shock and vibration makes them ideal for demanding applications in power plants, refineries, and industrial furnaces.
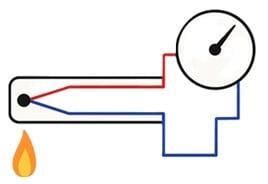
RTD Sensors
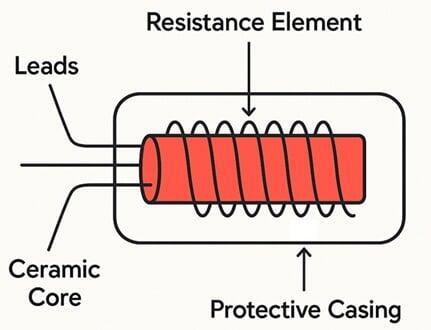
Application: RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors) provide precise and repeatable temperature measurement, typically using platinum elements such as PT100 or PT1000. They are preferred in applications requiring high accuracy and long-term stability, including pharmaceutical batch processing, food production lines, and cleanroom manufacturing. RTDs are often installed in sanitary fittings, thermowells, or industrial probes to monitor critical temperature parameters with tight tolerances.
Camera-Based Sensors

Industrial Glass Thermometer
Application: Industrial glass thermometers utilize liquid or gas expansion within a sealed system to measure temperature mechanically. These temperature gauges are well-suited for remote sensing locations where electrical power is not available or where environmental conditions call for a passive, mechanical approach. Typical applications include temperature control in air handling units, tank heating systems, and older industrial process setups where electronic components may not be viable.

Thermowells

Talk to an Expert
Temperature Transmitters
Analog & Digital Temperature Transmitters
Application: Analog temperature transmitters convert sensor inputs from RTDs or thermocouples into standardized 4–20 mA output signals for integration with PLCs, DCS, or panel meters. These transmitters are ideal for environments requiring high signal integrity over long cable distances, offering noise immunity and compatibility with legacy systems. Common applications include distributed process loops in refineries, water treatment facilities, and boiler control systems where simplicity, reliability, and low signal latency are critical.

Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS) Temperature Transmitters

Talk to an Expert
Temperature Switches
Mechanical Temperature Switches
Application: Mechanical temperature switches provide reliable, passive control in temperature-dependent processes by using physical mechanisms to trigger switching actions. These switches are widely used in HVAC systems, thermal protection circuits, and industrial heating and cooling equipment. Due to their simple construction and lack of electrical requirements for sensing, they are ideal for remote or hazardous environments where electrical components may be limited or undesired. Mechanical temperature switches offer robust operation in high-vibration settings and are often employed as primary or backup safety shutdown devices in thermal process systems.

Electronic Temperature Switches

Talk to an Expert
Temperature Gauges
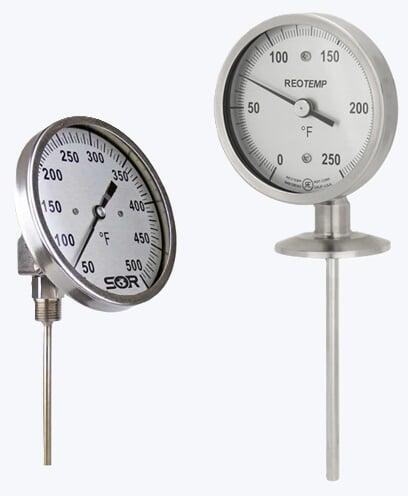
Bimetallic Temperature Gauges
Application: Bimetallic temperature gauges utilize the mechanical deflection of a coiled bimetallic strip to provide direct temperature indication without requiring external power. These gauges are ideal for rugged mechanical applications such as boilers, hydraulic systems, and HVAC equipment. Their robust construction ensures reliable performance in high-vibration environments, while their cost-effectiveness and simplicity make them well-suited for general-purpose temperature monitoring across a wide operating range.

Gas-Actuated Temperature Gauges
Application: Gas-actuated temperature gauges operate on the principle of pressure change within a sealed gas-filled system, enabling accurate temperature readings even over long capillary distances. With a fast response and stable readings across wide temperature ranges, these gauges are commonly used in tanks, pipelines, heat exchangers, and remote process locations. Their ability to maintain accuracy under harsh operating conditions makes them an excellent choice for applications in power generation, chemical processing, and heavy industry.

Liquid-Filled / Vapor-Tension Gauges

Digital Temperature Gauges

Talk to an Expert
Temperature Controllers
On/Off Temperature Controllers
Application: On/Off temperature controllers provide a basic form of thermal regulation by switching output devices fully on or off in response to temperature deviations from the setpoint. This binary control method is ideal for non-critical applications with slow thermal response, such as water heaters, food warming equipment, and small ovens. While cost-effective and easy to implement, On/Off control can result in temperature oscillation (hysteresis) around the setpoint and is generally not suitable for precision processes or systems with rapid thermal cycling.

Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Controllers

Programmable / Multi-Loop Controllers
Application: Programmable temperature controllers manage multiple independent or cascaded loops and often include advanced features such as ramp/soak profiling, data logging, alarm outputs, and recipe management. These controllers are used in batch processing, environmental test chambers, industrial kilns, and any system requiring time-based thermal control or process sequencing. With Ethernet, Modbus, and analog output options, they can operate as standalone logic units or as part of a distributed control system. Their scalability and configurability make them a flexible solution for complex thermal control environments.

Safety Limit Controllers (High-Limit / Low-Limit)

Talk to an Expert
Need Help?
Our Crew is Here To Serve You!
Temperature Instrumentation Applications
Municipal Water & Wastewater Treatment Applications
Temperature monitoring is essential across many stages of water and wastewater treatment to optimize performance, protect equipment, and meet regulatory standards. Below are key applications along with the types of temperature instrumentation commonly used:
- Biological Treatment Processes (Aeration & Activated Sludge)
Purpose: Monitor basin temperature to ensure optimal microbial activity and biological reaction rates.
Instrumentation Used: RTD sensors or thermocouples integrated with transmitters for continuous monitoring. Data is typically fed into SCADA or PLC systems for trend analysis and process optimization. - Anaerobic Digestion
Purpose: Maintain proper temperature within digesters to support methane production and stable digestion performance.
Instrumentation Used: High-accuracy RTDs with thermowells, paired with PID controllers or temperature transmitters. Monitoring is critical for both mesophilic and thermophilic digestion regimes. - Disinfection & Chlorination
Purpose: Adjust chemical dosing based on temperature, as disinfection efficacy can vary with water temperature.
Instrumentation Used: Compact RTDs or thermistors with transmitters used to provide real-time temperature data for chemical feed control logic. - Sludge Treatment & Dewatering
Purpose: Monitor and control temperature during sludge thickening and thermal conditioning to improve solids handling and energy recovery.
Instrumentation Used: Industrial-grade RTDs with remote transmitters or local indicators installed in sludge lines or thermal treatment chambers. - Effluent Monitoring & Environmental Compliance
Purpose: Track final effluent temperature prior to discharge to comply with thermal pollution limits and NPDES permit requirements.
Instrumentation Used: In-line thermocouples or immersion sensors with data logging capabilities. Often integrated into compliance monitoring systems. - Freeze Protection & Equipment Monitoring
Purpose: Detect low ambient or process temperatures to trigger heat tracing or insulation systems, protecting exposed piping and tanks.
Instrumentation Used: Temperature switches and simple on/off controllers tied to local alarm systems or automated heat systems.
Food & Beverage Processing Applications
Temperature control is critical throughout the food and beverage production chain to ensure product quality, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. From raw material handling to packaging, temperature impacts food safety, shelf stability, and process performance. Below are key applications along with the types of temperature instrumentation commonly used:
- Pasteurization & Sterilization
Purpose: Ensure that temperature reaches and maintains required thresholds to eliminate harmful microorganisms and extend shelf life.
Instrumentation Used: High-accuracy RTDs or sanitary thermocouples installed in process lines and heat exchangers, often paired with PID controllers and data loggers to meet HACCP and FDA validation requirements. - Cooking, Baking, and Thermal Processing
Purpose: Maintain precise temperature profiles for consistent product texture, flavor, and doneness across batches.
Instrumentation Used: Insertion thermocouples and RTDs with programmable controllers and ramp/soak capabilities to follow time-temperature recipes. Infrared sensors may be used for non-contact surface monitoring in conveyor ovens. - Fermentation & Culturing
Purpose: Monitor and control temperature in fermentation tanks to support microbial growth and biochemical reactions.
Instrumentation Used: Sanitary RTDs or thermistors integrated into fermentation vessels with temperature transmitters and local or remote PID controllers for tight regulation. - Chilling & Freezing
Purpose: Rapidly reduce temperature of products to inhibit microbial growth and preserve freshness.
Instrumentation Used: Thermocouples or RTDs used in blast chillers, freezers, and glycol systems, often tied to SCADA systems or refrigeration controls to monitor system response and ensure cold chain integrity. - CIP (Clean-in-Place) Systems
Purpose: Verify that cleaning cycles reach required temperatures to ensure sanitation of tanks, piping, and process equipment.
Instrumentation Used: RTDs in hygienic fittings with digital transmitters and data acquisition systems for traceability and validation of thermal cleaning cycles. - Packaging & Sealing Operations
Purpose: Control sealing temperatures to ensure proper packaging integrity and prevent spoilage or contamination.
Instrumentation Used: Embedded thermocouples with high-speed controllers on heat-sealing equipment, ensuring consistent performance and reducing waste. - Storage & Cold Chain Monitoring
Purpose: Monitor storage conditions for temperature-sensitive products during warehousing and transportation.
Instrumentation Used: Wireless temperature sensors, data loggers, and digital gauges installed in refrigerated storage and transport units to maintain compliance and quality assurance.
Life Science & Pharmaceutical Applications
- Bioreactors & Fermentation Vessels
Purpose: Maintain tightly controlled temperature environments to optimize biological growth and reaction kinetics during cell culture and fermentation.
Instrumentation Used: High-accuracy RTDs in hygienic fittings, often with redundant sensors and transmitters integrated into validated control systems. PID controllers with alarm and logging functions are standard to ensure stability and traceability. - Lyophilization (Freeze-Drying)
Purpose: Monitor and control temperature during sublimation and secondary drying phases to protect product structure and efficacy.
Instrumentation Used: Thermocouples with high-speed controllers and data acquisition systems are used inside freeze-dry chambers. Sensor mapping and validation procedures ensure uniform temperature profiles during critical drying stages. - Cold Storage & Vaccine Freezers
Purpose: Ensure temperature stays within strict limits for storage of temperature-sensitive drugs, vaccines, and biologics.
Instrumentation Used: RTDs or thermistors connected to wireless transmitters or data loggers. Alarm systems with SMS/email notification and cloud integration are common for compliance with CDC and WHO cold chain requirements. - Autoclaves & Sterilization Chambers
Purpose: Verify that sterilization cycles meet temperature and exposure time requirements for validated cleaning and decontamination.
Instrumentation Used: Thermocouples or RTDs placed in load probes and chamber walls, connected to validated controllers and monitoring systems. Redundant sensors and independent safety limit controllers are often used for added assurance. - Cleanroom Environmental Monitoring
Purpose: Monitor ambient temperature in cleanroom environments to maintain consistent conditions and meet GMP or ISO standards.
Instrumentation Used: Wall-mounted RTDs or digital temperature sensors with BACnet or Modbus communication. Integrated into building management systems (BMS) with continuous logging and audit trail capabilities. - Research & Stability Chambers
Purpose: Simulate long-term storage and shelf-life conditions for pharmaceuticals under controlled temperature profiles.
Instrumentation Used: RTDs with transmitters tied into programmable environmental chambers, featuring multi-point mapping and precise ramp/soak control for stability studies and ICH compliance. - WFI (Water for Injection) Systems
Purpose: Monitor hot water temperatures to ensure compliance with USP and EU Pharmacopoeia standards for WFI generation and distribution.
Instrumentation Used: Sanitary RTDs or thermocouples installed in-line with transmitters. Data logging and SCADA integration provide validation-ready temperature records.
Power Generation & Energy Applications
- Turbine Inlet & Exhaust Monitoring
Purpose: Measure combustion and exhaust temperatures to protect turbine components, optimize performance, and comply with emissions standards.
Instrumentation Used: High-temperature thermocouples (e.g., Type K or N) installed at critical monitoring points, often with rugged protection sheaths and fast-response tips. Data is transmitted to DCS or turbine control systems for real-time diagnostics and performance tuning. - Boiler and Steam Drum Monitoring
Purpose: Maintain precise temperature control in water walls, steam drums, and superheaters to optimize steam quality and thermal efficiency.
Instrumentation Used: Thermocouples and RTDs in high-pressure wells or welded fittings, with 4–20 mA transmitters integrated into safety interlocks and closed-loop controls. - Heat Recovery Steam Generators (HRSGs)
Purpose: Monitor flue gas and feedwater temperatures to manage thermal gradients and avoid material fatigue in combined cycle plants.
Instrumentation Used: Multiple point thermocouple arrays and RTDs, monitored via programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or distributed control systems (DCS). Temperature switches are also used for high-temperature trip alarms. - Generator Bearing & Winding Temperature
Purpose: Detect overheating in generator bearings, stators, and windings to prevent insulation failure and unplanned outages.
Instrumentation Used: Embedded RTDs or thermistors with digital transmitters. Temperature limit controllers are often included for shutdown protection or alarm signaling. - Thermal Energy Storage & Solar Thermal Systems
Purpose: Regulate heat transfer fluid (HTF) and molten salt temperatures to maximize energy storage capacity and system efficiency.
Instrumentation Used: RTDs with remote-mount transmitters designed for extreme temperatures and corrosive fluids. Instruments are often networked for control room visibility and SCADA integration. - Transformer & Substation Monitoring
Purpose: Measure oil and winding temperatures to assess transformer load conditions and extend asset life.
Instrumentation Used: Analog and digital temperature gauges, RTDs, and thermal switches installed in transformer tanks. Data is transmitted via hardwired or wireless condition monitoring systems. - Cooling Water Systems & Condensers
Purpose: Monitor inlet and outlet temperatures to assess heat exchanger performance and prevent fouling or scaling.
Instrumentation Used: Insertion RTDs and thermocouples with weatherproof transmitters and local displays. Often connected to automated blowdown or chemical treatment systems.
Chemical & Petrochemical Applications
- Reaction Vessel Monitoring
Purpose: Control exothermic and endothermic reactions by maintaining precise temperature profiles within reactors.
Instrumentation Used: RTDs or thermocouples installed in thermowells or jacketed vessels. Often paired with PID controllers and remote-mount transmitters connected to DCS systems for closed-loop control. - Distillation Columns
Purpose: Monitor column temperature gradients to optimize separation efficiency and control overhead and bottom product purity.
Instrumentation Used: Multipoint thermocouple assemblies or RTDs installed at strategic column locations, with data integrated into advanced process control systems. - Heat Exchangers
Purpose: Ensure efficient heat transfer and detect fouling or scaling conditions by monitoring inlet and outlet temperatures.
Instrumentation Used: Insertion-style RTDs or thermocouples, typically installed in both process and utility streams. Transmitters feed data into plant-wide performance monitoring systems. - Tank Heating & Temperature Maintenance
Purpose: Maintain storage tank temperatures to prevent product solidification or phase separation, especially for high-viscosity chemicals.
Instrumentation Used: Thermocouples or RTDs installed through tank walls or in thermal wells, with feedback to temperature switches or local control panels to regulate electric heat tracing or steam systems. - Emissions & Flare Stack Monitoring
Purpose: Measure combustion efficiency and temperature at the flare tip to ensure safe operation and compliance with emissions regulations.
Instrumentation Used: Infrared temperature sensors or high-range thermocouples in thermowells with flame arrestors. Data is logged and used for combustion diagnostics and EPA reporting. - Pipelines & Process Lines
Purpose: Monitor temperature to detect line blockages, freezing, or reaction zone stability in continuous processes.
Instrumentation Used: Inline RTDs or clamp-on thermocouples, often paired with wireless transmitters or local indicators in hazardous-rated enclosures. - Batch Reactor Safety Systems
Purpose: Provide over-temperature protection in batch reactors to prevent thermal runaway and equipment damage.
Instrumentation Used: SIL-rated temperature switches or limit controllers with redundant RTDs, integrated into safety interlock systems per IEC 61508/61511 standards.
Mining & Minerals Processing Applications
In mining and mineral processing operations, temperature measurement is essential for maintaining process stability, ensuring worker safety, and protecting equipment from thermal stress. From ore extraction and material separation to drying and smelting, reliable temperature instrumentation helps optimize yield, reduce energy consumption, and improve system uptime. Below are key applications and the instrumentation used:
- Ore Drying and Rotary Kilns
Purpose: Monitor and control material and shell temperatures to ensure proper drying, calcining, or roasting in rotary kilns and dryers.
Instrumentation Used: High-temperature thermocouples installed at multiple kiln zones, paired with transmitters and PID controllers. Infrared sensors may be used for non-contact shell temperature measurement. - Flotation and Leaching Tanks
Purpose: Maintain optimal temperature conditions for chemical reactions and separation efficiency during flotation or leaching.
Instrumentation Used: RTDs or thermistors in protective wells, integrated with local displays or control systems. Monitoring supports reagent activity and enhances mineral recovery. - Autoclaves and Pressure Oxidation Reactors
Purpose: Monitor internal temperatures under high pressure to ensure reaction control and metallurgical recovery in hydrometallurgical processes.
Instrumentation Used: High-pressure thermowell assemblies with RTDs or thermocouples rated for extreme conditions, integrated into DCS systems with alarm and interlock capabilities. - Slurry Transport Lines
Purpose: Detect temperature changes to prevent settling, monitor viscosity, and protect against freeze conditions in slurry pipelines.
Instrumentation Used: Clamp-on RTDs or insertion-style thermocouples, often in rugged housings with remote transmitters for hazardous or remote locations. - Crushing and Conveying Systems
Purpose: Monitor bearing, motor, and gearbox temperatures to prevent overheating and mechanical failure in crushers and conveyor belts.
Instrumentation Used: Embedded RTDs or surface-mounted thermocouples with alarm relays or temperature switches for shutdown protection. - Smelting and Furnace Operations
Purpose: Control melt zone temperatures and ensure safe furnace operation during metal extraction and refining.
Instrumentation Used: High-range thermocouples (Type B, R, or S) used in refractory-lined wells or immersion assemblies. Data is transmitted to furnace control systems for real-time adjustment. - Environmental and Worker Safety Monitoring
Purpose: Track ambient temperatures in underground tunnels and high-temperature work zones to maintain safe operating conditions.
Instrumentation Used: Digital temperature gauges or thermistor-based sensors with wireless transmitters and integration into mine ventilation or safety systems.
Data Center Applications
In data centers, precise temperature monitoring is essential for maintaining system uptime, reducing energy costs, and protecting critical IT infrastructure. With increasing server densities and heat loads, modern facilities depend on accurate, real-time thermal data to optimize cooling strategies and prevent hardware failures. Below are key applications and the instrumentation used:
- Rack-Level Temperature Monitoring
Purpose: Monitor inlet and exhaust air temperatures at the server rack level to detect thermal hotspots and ensure consistent cooling across rows.
Instrumentation Used: Digital temperature sensors or thermistor probes installed in rack-mounted units or on blanking panels. Often networked via Modbus, BACnet, or SNMP for integration into DCIM or BMS platforms. - CRAC and CRAH Unit Control
Purpose: Maintain precise temperature setpoints for Computer Room Air Conditioners (CRAC) or Air Handlers (CRAH) to ensure proper air supply and return conditions.
Instrumentation Used: High-resolution RTDs or digital sensors placed at air intakes and return ducts. Paired with PID controllers or BMS-controlled actuators to regulate cooling output. - Underfloor Plenum and Aisle Monitoring
Purpose: Track airflow temperatures in raised floor plenums and cold/hot aisle containment zones to manage airflow distribution and eliminate recirculation.
Instrumentation Used: Compact thermistors or digital sensors on mounting rails or support structures, feeding real-time data to airflow balancing or optimization systems. - Chilled Water System Monitoring
Purpose: Ensure efficient operation of chilled water loops used in data center cooling infrastructure, including air handlers and in-row cooling units.
Instrumentation Used: Insertion-style RTDs or thermocouples placed in supply and return lines. Data is used for load tracking, pump control, and efficiency analytics. - Liquid Cooling and Rear Door Heat Exchangers
Purpose: Control coolant loop temperatures in direct-to-chip cooling systems or rear door heat exchangers to protect high-density computing hardware.
Instrumentation Used: RTDs or thermistors embedded in liquid manifolds or quick-connect fittings, integrated with cooling distribution unit (CDU) controllers. - Power Distribution Equipment
Purpose: Monitor transformer, UPS, and PDU temperatures to detect overheating and prevent electrical faults.
Instrumentation Used: Surface-mount RTDs or thermocouples with alarm relays or smart transmitters. Often tied into predictive maintenance or facility monitoring systems. - Ambient and Redundancy Monitoring
Purpose: Provide room-level temperature monitoring and redundancy in critical spaces to prevent blind spots in thermal coverage.
Instrumentation Used: Wall-mounted digital temperature gauges or wireless sensors with battery backup, reporting data to cloud-based dashboards or local control systems.
Terms & Definitions
SIL (Safety Integrity Level)
Span
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Clipper Controls provide help with selecting the right temperature instrumentation?
Yes. Our technical team works closely with you to understand your application and recommend the most appropriate sensor, transmitter, controller, or protection hardware for your environment.
What is the difference between an RTD and a thermocouple?
RTDs offer high accuracy and long-term stability, making them ideal for precision applications. Thermocouples have a wider temperature range and faster response times, making them better suited for high-temperature or fast-changing environments.
When should I use a thermowell?
What type of temperature transmitter should I choose?
How accurate are bimetallic temperature gauges?
Bimetallic gauges are generally accurate to ±1–2% of full scale, which is suitable for many industrial and mechanical applications. For higher accuracy, consider a digital or RTD-based system.
Can I use a temperature controller for both heating and cooling?
Yes. Many modern controllers support dual-action control and can manage heating and cooling outputs simultaneously or with independent setpoints.
What’s the purpose of a safety limit controller?
Safety limit controllers serve as a last line of defense. They shut down equipment if temperature exceeds a predefined limit, protecting both assets and personnel. They are often required in regulated or SIL-rated environments.
Do temperature switches require power?
Mechanical temperature switches (such as bimetal or liquid-filled bulb types) operate without external power. Electronic switches, however, require power and offer features like digital displays or relay outputs.
Need Help?
Our Crew is Here To Serve You!
Services We Offer
Instrumentation Calibrations
Rental Equipment
Equipment Troubleshooting
Repairs & Maintenance
Instrumentation
Flow Studies
Startup & Training
Products We Offer
Resources
- Thermocouple Tables
- RTD Tables



