Non-Targeted Analysis of Water and Biosolids
Mass spectrometry chemical fingerprint reveals unknown chemistry driving upsets
👉 Ready to see what’s really in your influent or biosolids?
Contact Clipper Controls to launch a non-targeted analysis pilot.
Explore Similar Pages: Automatic Water Samplers | Sewer Flow Meters | Water & Wastewater Treatment Process Control Solutions | Metering Manholes | Environmental Monitoring Systems | Wastewater-Based Epidemiology and Epidemic Preparedness | Fiberglass (FRP) Shelters for Instrumentation & Analyzers | Industrial Gas Detectors for Toxic & Combustible Gas Monitoring
Why Traditional Monitoring No Longer Tells the Full Story
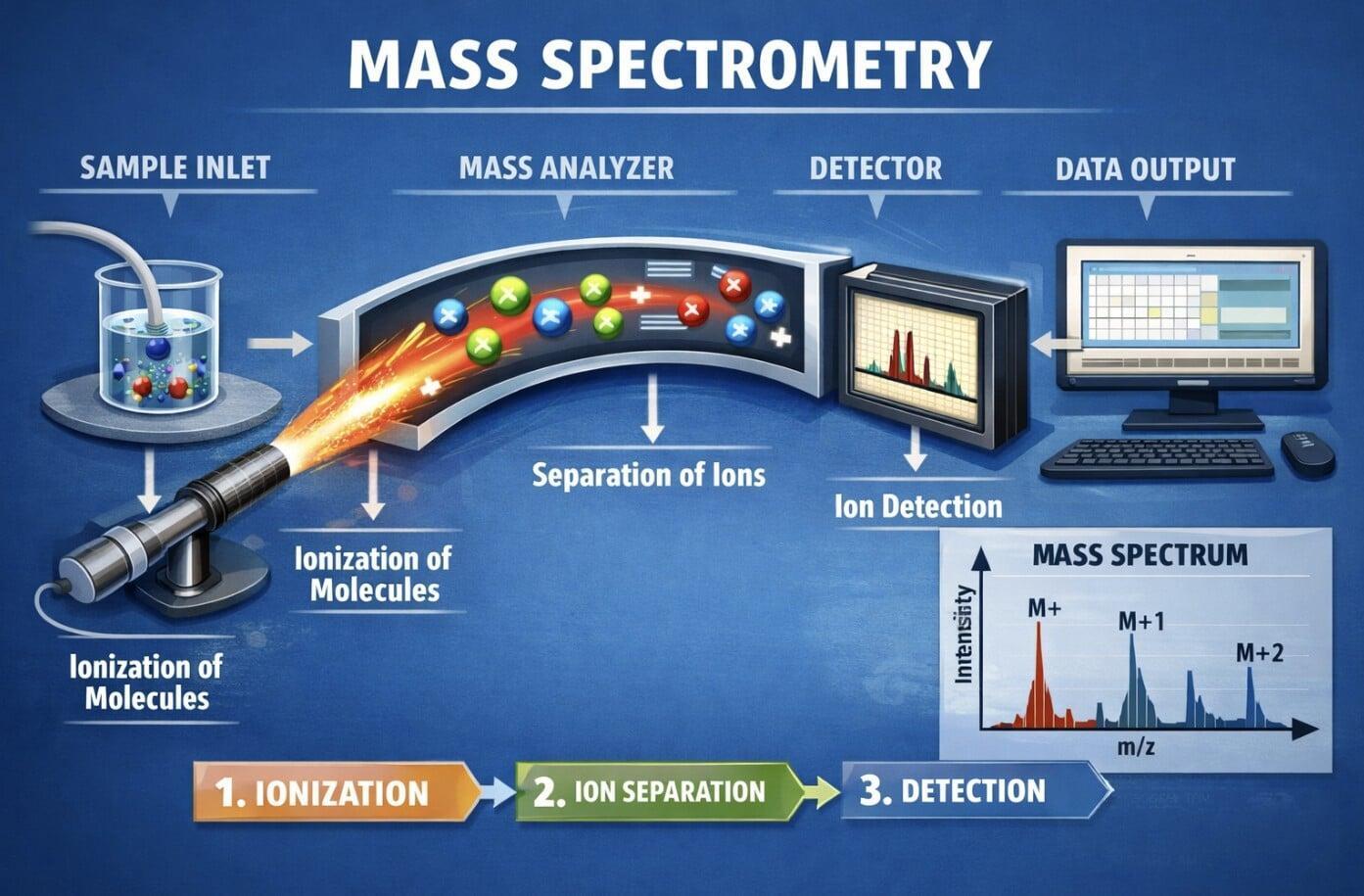
What Is Non-Targeted Analysis (NTA)?
Clipper Controls works with CEC Innovations (cecinnovations.com) to deliver non-targeted analysis services to customers in California, Nevada, and Hawaii. CEC Innovations performs the mass spectrometry analysis and applies their exhaustive database to link identified compounds to known product sources and treatment impacts. Clipper Controls supports customers with sampling strategy, program setup, and access to ongoing analytical consulting through CEC Innovations.
From Raw Chemistry to Operational Intelligence
- What the compound is
- Where it originated (industrial, commercial, residential, environmental)
- How it impacts treatment processes or environmental outcomes
- This transforms analytical output into information operators can use.
Source Attribution
Functional Use Classification
Treatment Impact Analysis
Management Insights
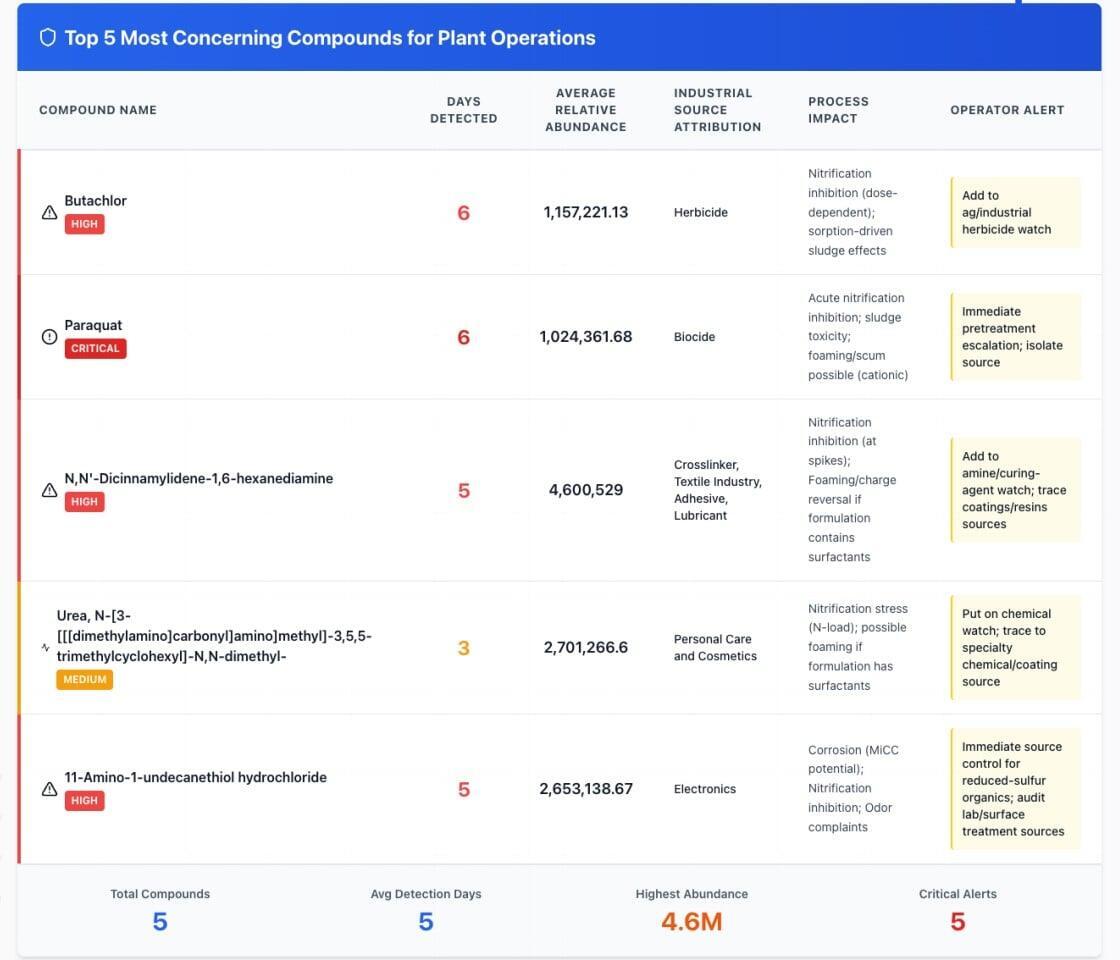
Seeing the Drivers Behind Treatment Upsets
Most treatment upsets are not random events. They are driven by changes in influent chemistry that traditional monitoring cannot see.

👉 Trying to troubleshoot unexplained discharge variability or strengthen pretreatment? Call (844) 880-2469 or message us to explore non-targeted analysis for industrial discharge monitoring.
Quantifying What’s Really Driving BOD, COD, and Oxygen Demand
BOD and COD are essential metrics, but they do not explain what is creating the load. NTA calculates ThOD (Theoretical Oxygen Demand) on a per-compound basis, showing which compounds contribute most to biological stress and where they originate.
This compound-level insight supports pretreatment optimization, evidence-based surcharge programs, and influent/effluent comparisons that reveal how treatment performance changes across the process.
PFAS, Source Protection, and Regulatory Readiness
PFAS compounds are persistent, mobile, and difficult to treat. For most utilities, source protection is the only viable long-term strategy.
NTA detects PFAS within the broader chemical fingerprint, applies industrial source categories, and supports early intervention before concentrations escalate. Sampling throughout the treatment train also reveals whether PFAS remains in the aqueous phase or partitions into sludge and biosolids—critical information for planning around current and upcoming regulations.
Odor, H₂S, and Localized Collection System Insights
Odor and hydrogen sulfide issues are among the most persistent challenges in collection systems—and among the hardest to diagnose with traditional tools.
NTA identifies odor-causing and sulfur-related compounds directly and supports localized sampling at lift stations, interceptors, and upstream nodes. This enables targeted, data-driven treatment strategies rather than blanket chemical dosing, reducing cost and improving effectiveness.
How NTA Works in Practice
NTA is designed to integrate easily into existing workflows.

Why Trend Data Matters More Than Single Samples
Single samples provide snapshots. Trend data provides understanding.
By analyzing trends over time, utilities can identify emerging risks, distinguish isolated anomalies from systemic issues, prepare for contamination spikes, and intervene before upsets or violations occur. Trend-based monitoring supports confident planning in systems where chemistry is constantly changing.
Who Benefits From Non-Targeted Analysis?
- Municipal wastewater utilities
- Industrial pretreatment programs
- Industrial and commercial dischargers
- Environmental and engineering consultants
- Collection systems and decentralized or package treatment plants
Pairing NTA With Sampling & Instrumentation
NTA complements—rather than replaces—existing monitoring programs.
Automatic water samplers ensure representative data, while continuous analyzers provide real-time awareness. NTA explains why changes occur, enhancing the value of instrumentation by adding chemical context to alarms, trends, and performance shifts.
Supporting Modern Water Challenges With Modern Solutions
How Clipper Controls Supports Advanced Water Intelligence
Clipper Controls helps utilities and industries bridge the gap between monitoring and understanding. By pairing advanced sampling strategies, instrumentation, and non-targeted analysis, Clipper Controls supports stronger pretreatment programs, improved response to treatment upsets, and smarter planning for emerging contaminants.
👉 Ready to start a NTA pilot program? We can help!
Message Clipper Controls or call (844) 880-2469 to put together a “sample + analysis” NTA program for influent, lift stations, effluent, or biosolids.

Frequently Asked Questions
There are no preservatives and no fixed hold time. Keep the sample on ice from collection through shipping (the sample kit includes ice packs). As long as the sample remains cold, it’s acceptable for analysis.
A mass spectrometry-based method that captures a full chemical fingerprint of water or biosolids and turns it into operational insight.
Targeted testing looks for a set list of known compounds. NTA reveals thousands of compounds present—including unknown and emerging substances.
A comprehensive specialized proprietary database that links identified compounds to likely product sources and expected treatment impacts.
Typically tens of thousands of organic compounds per sample.
No. It focuses on organic compounds.
Yes. Results include source attribution (industrial, commercial, residential, environmental) based on detected compounds.
It flags compound patterns associated with foaming, inhibition, toxicity, oxygen transfer issues, and other drivers of instability.
Yes. It can estimate ThOD (Theoretical Oxygen Demand) per compound to clarify what’s driving load and from where.
Yes. PFAS can appear within the fingerprint, supporting source protection and planning for regulations.
Influent, effluent, lift stations, interceptors, upstream collection nodes, industrial discharge points, and biosolids/sludge streams.
A common pilot is 15–20 samples over several weeks to capture trends, not just snapshots.
$250 per sample, including the report and dashboard access.
Municipal utilities, industrial pretreatment teams, industrial dischargers, consultants, and decentralized/package systems.
No. It complements them by explaining the “why” behind trends and alarms.
By helping connect sampling strategy, monitoring tools, and actionable interpretation so teams can respond with confidence.
Page Navigation Links
- Why Traditional Monitoring No Longer Tells the Full Story
- What Is Non-Targeted Analysis (NTA)?
- Seeing the Drivers Behind Treatment Upsets
- Quantifying What's Really Driving BOD, COD, and Oxygen Demand
- PFAS, Source Protection, and Regulatory Readiness
- Odor, H₂S, and Localized Collection System Insights
- How NTA Works in Practice
- Why Trend Data Matters More Than Single Samples
- Who Benefits From Non-Targeted Analysis?
- Pairing NTA With Sampling & Instrumentation
- Supporting Modern Water Challenges With Modern Solutions
- How Clipper Controls Supports Advanced Water Intelligence
